Decimal to Binary Conversion (20.1.5)
It is also necessary to understand how to convert a dotted decimal IPv4 address to binary. A useful tool is the binary positional value table, as shown in Figure 20-3 through 20-10.
In Figure 20-3, is the decimal number of the octet (n) equal to or greater than the most-significant bit (128)?
• If no, then enter binary 0 in the 128 positional value.
• If yes, then add a binary 1 in the 128 positional value and subtract 128 from the decimal number.
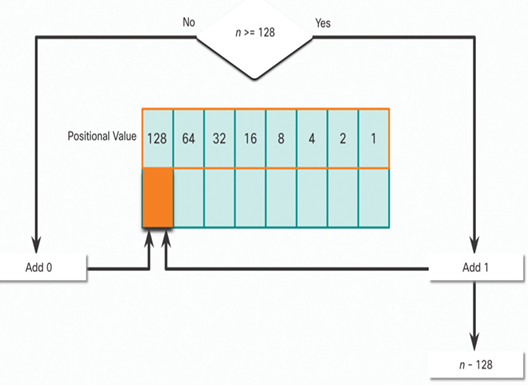
Figure 20-3 128 Positional Value
In Figure 20-4, is the decimal number of the octet (n) equal to or greater than the next most-significant bit (64)?
• If no, then enter binary 0 in the 64 positional value.
• If yes, then add a binary 1 in the 64 positional value and subtract 64 from the decimal number.
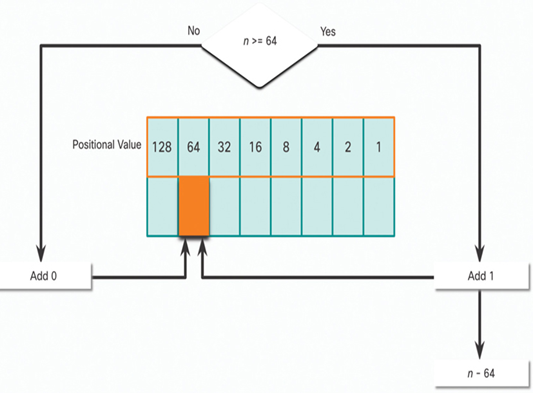
Figure 20-4 64 Positional Value
In Figure 20-5, is the decimal number of the octet (n) equal to or greater than the next most-significant bit (32)?
• If no, then enter binary 0 in the 32 positional value.
• If yes, then add a binary 1 in the 32 positional value and subtract 32 from the decimal number.
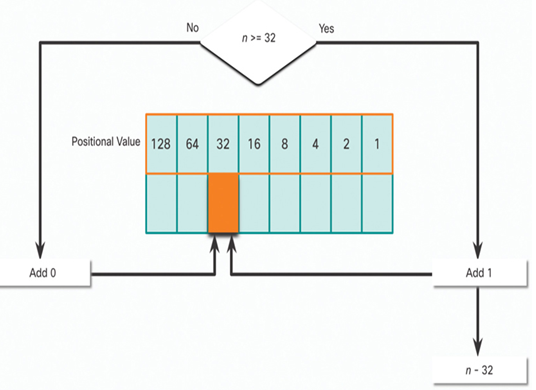
Figure 20-5 32 Positional Value
In Figure 20-6, is the decimal number of the octet (n) equal to or greater than the next most-significant bit (16)?
• If no, then enter binary 0 in the 16 positional value.
• If yes, then add a binary 1 in the 16 positional value and subtract 16 from the decimal number.
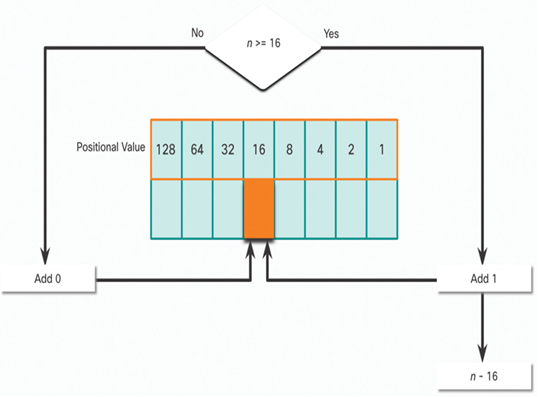
Figure 20-6 16 Positional Value
In Figure 20-7, is the decimal number of the octet (n) equal to or greater than the next most-significant bit (8)?
• If no, then enter binary 0 in the 8 positional value.
• If yes, then add a binary 1 in the 8 positional value and subtract 8 from the decimal number.
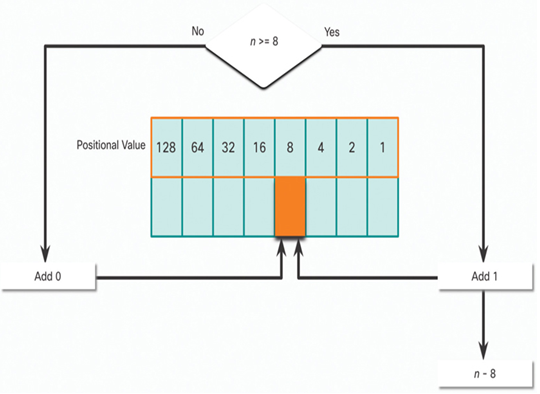
Figure 20-7 8 Positional Value
In Figure 20-8, is the decimal number of the octet (n) equal to or greater than the next most-significant bit (4)?
• If no, then enter binary 0 in the 4 positional value.
• If yes, then add a binary 1 in the 4 positional value and subtract 4 from the decimal number.
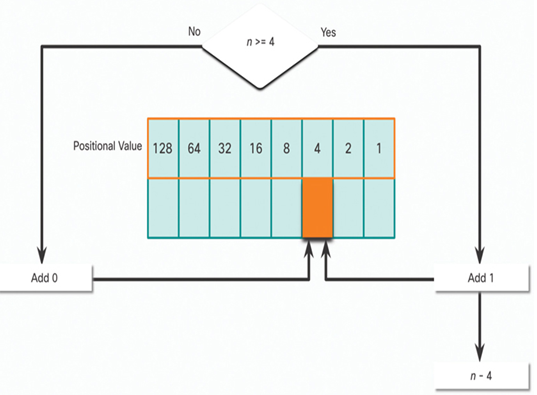
Figure 20-8 4 Positional Value
In Figure 20-9, is the decimal number of the octet (n) equal to or greater than the next most-significant bit (2)?
• If no, then enter binary 0 in the 2 positional value.
• If yes, then add a binary 1 in the 2 positional value and subtract 2 from the decimal number.
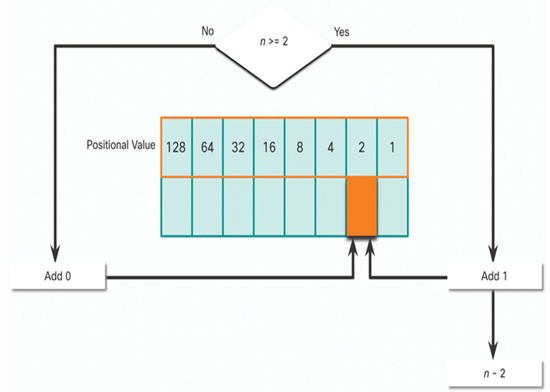
Figure 20-9 2 Positional Value
In Figure 20-10, is the decimal number of the octet (n) equal to or greater than the last most-significant bit (1)?
• If no, then enter binary 0 in the 1 positional value.
• If yes, then add a binary 1 in the 1 positional value and subtract 1 from the last decimal number.
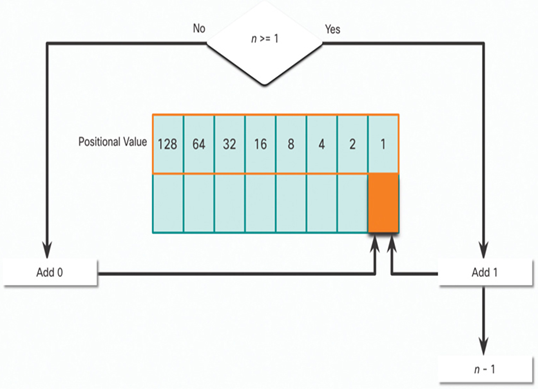
Figure 20-10 1 Positional Value
