Upon completion of this chapter, you will be able to answer the following questions:
• What is the operation of IPv6 neighbor discovery?
There are no new terms in this chapter.
Webster here!
Halimah is still investigating her company’s network. She is impressed with the way the IT team has structured it. She knows about IPv6 neighbor discovery (ND) and, in this module, you will learn about it too.
IPv6 ND is how IPv6-addressed devices resolve MAC addresses. IPv6 ND lets devices with IPv6 addresses communicate with other devices on a network, which is, let’s face it, the whole reason for having a network.
So, given how important this subject is, let’s get started!
Neighbor Discovery Operation (34.1)
This section discusses the relationship between MAC and IPv6 addresses, and the how the Neighbor Discovery (ND) protocol is used to map the two addresses.
Video – IPv6 Neighbor Discovery (34.1.1)
If your network is using the IPv6 communications protocol, the Neighbor Discovery protocol, or ND, is what you need to match IPv6 addresses to MAC addresses. This topic explains how ND works.
Refer to the online course to view this video.
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Messages (34.1.2)
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery protocol is sometimes referred to as ND or NDP. In this course, we will refer to it as ND. ND provides address resolution, router discovery, and redirection services for IPv6 using ICMPv6. ICMPv6 ND uses five ICMPv6 messages to perform these services:
- Neighbor Solicitation messages
- Neighbor Advertisement messages
- Router Solicitation messages
- Router Advertisement messages
- Redirect Message
Neighbor Solicitation and Neighbor Advertisement messages are used for device-to-device messaging such as address resolution (similar to ARP for IPv4). Devices include both host computers and routers, as shown if Figures 34-1 and 34-2.
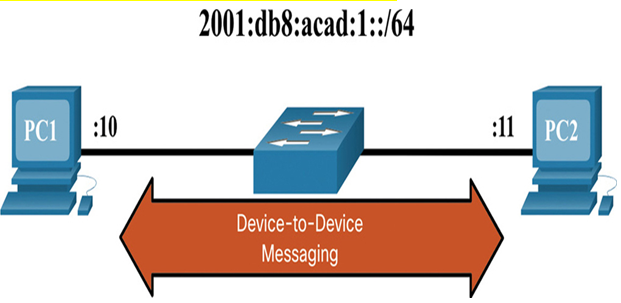
Figure 34-1 Device-to-Device Messaging
Router Solicitation and Router Advertisement messages are for messaging between devices and routers. Typically router discovery is used for dynamic address allocation and stateless address autoconfiguration (SLAAC).
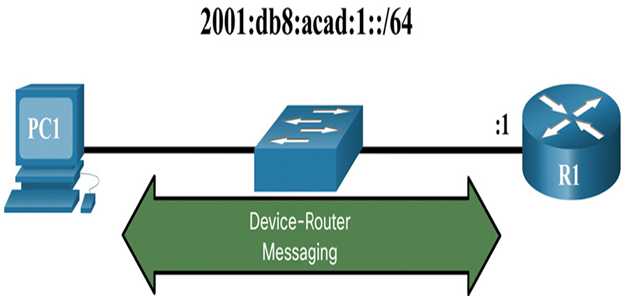
Figure 34-2 Device-Router Messaging
Note:
The fifth ICMPv6 ND message is a redirect message which is used for better next-hop selection. This is beyond the scope of this course.
IPv6 ND is defined in the IETF RFC 4861.
IPv6 Neighbor Discovery — Address Resolution (34.1.3)
Much like ARP for IPv4, IPv6 devices use IPv6 ND to determine the MAC address of a device that has a a known IPv6 address.
ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicitation and Neighbor Advertisement messages are used for MAC address resolution. This is similar to ARP Requests and ARP Replies used by ARP for IPv4. For example, assume PC1 wants to ping PC2 at IPv6 address 2001:db8:acad::11. To determine the MAC address for the known IPv6 address, PC1 sends an ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicitation message as illustrated in Figure 34-3.
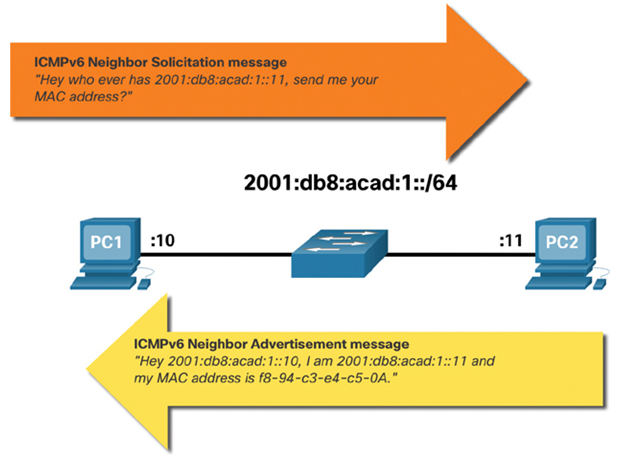
Figure 34-3 IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Process
ICMPv6 Neighbor Solicitation messages are sent using special Ethernet and IPv6 multicast addresses. This allows the Ethernet NIC of the receiving device to determine whether the Neighbor Solicitation message is for itself without having to send it to the operating system for processing.
PC2 replies to the request with an ICMPv6 Neighbor Advertisement message which includes its MAC address.
Packet Tracer – IPv6 Neighbor Discovery (34.1.4)
In order for a device to communicate with another device, the MAC address of the destination device must be known. With IPv6, a process called Neighbor Discovery is responsible for determining the destination MAC address. You will gather PDU information in simulation mode to better understand the process. There is no Packet Tracer scoring for this activity.
Refer to the online course to complete this Activity.
Check Your Understanding – Neighbor Discovery (34.1.5)
Refer to the online course to complete this Activity.
The following is a summary of each topic in the chapter and some questions for your reflection.
Neighbor Discovery IPv6 does not use ARP, it uses the ND protocol to resolve MAC addresses. ND provides address resolution, router discovery, and redirection services for IPv6 using ICMPv6. ICMPv6 ND uses five ICMPv6 messages to perform these services: neighbor solicitation, neighbor advertisement, router solicitation, router advertisement, and redirect. Much like ARP for IPv4, IPv6 devices use IPv6 ND to resolve the MAC address of a device to a known IPv6 address.
