At the time of writing in April 2023, Google Cloud is currently available in 37 regions, with a total of 112 separate zones and 176 network edge locations, and it operates in 200+ countries and territories.
By the time you read this book, Google Cloud will have expanded into other regions. You can visit the following URL to check where it operates at a given time: https://cloud.google.com/about/locations
As a global cloud provider, Google Cloud ensures to locate the resources closest to its users and their businesses. Google Cloud is heavily investing in its global presence and its expansion plans into new regions confirm this. At the time of writing, Google Cloud offers at a minimum the following products at launch:
- Google Compute Engine (GCE)
- Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE)
- Cloud Storage
- Persistent Disk
- Cloud SQL
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
- Key Management Service
- Cloud Identity
- Secret Manager
Other Google Cloud products will continue to evolve based on the demand from customers.
In the following figure (the original image can be found here: https://cloud.google.com/images/locations/regions.png), we can see Google Cloud’s global presence, including the existing and planned regions for 2023. It is worth mentioning that Google Cloud splits each region into three separate zones:
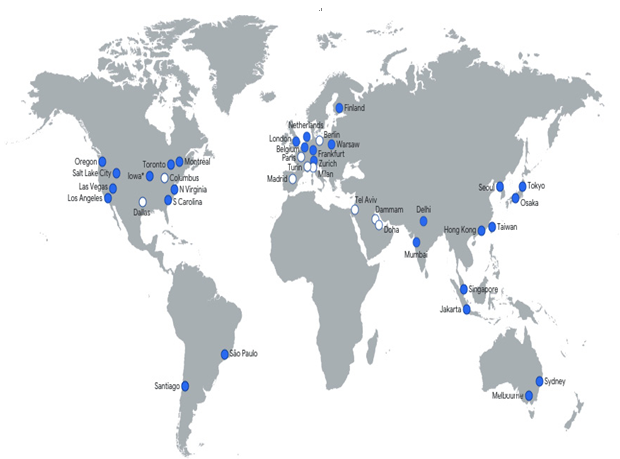
Figure 2.1 – Google Cloud regions across the world
Regions are just part of the Google Cloud presence. All regions are connected with each other via global networks and Content Delivery Network (CDN) points of presence.
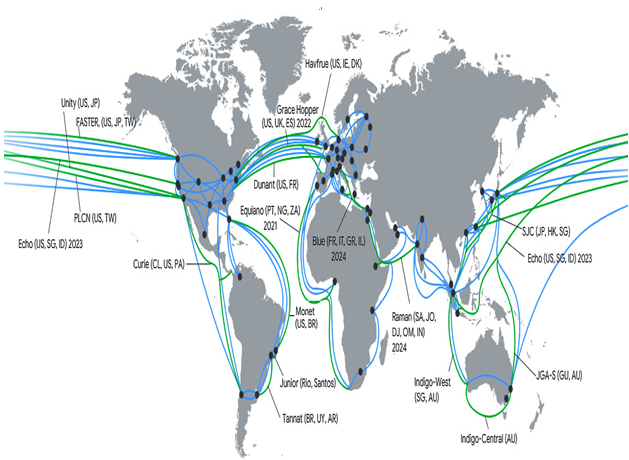
Figure 2.2 – Google Cloud Edge points of presence across the world
To view current Google Cloud locations, visit the website https://cloud.google.com/about/locations.
What makes Google Cloud different?
There is no right answer to this question because every customer and business is different and has different requirements. We have gathered differentiators that might be the most common ones. Let’s have a look at them:
- Google-grade security
- Google has managed their infrastructure for more than 15 years and this experience has allowed them to keep customers safe when using applications such as Gmail or Google Apps. Google Cloud is based on this experience and provides additional security products for customers.
- Billing by the second
- GCE instances use a 1-second billing feature that allows customers to only pay for used resources.
- Big data
- Innovation is the core principle of Google and this has led not only to technological innovations such as MapReduce, Bigtable, and Dremel but also next-generation services for cloud data warehousing (BigQuery), advanced ML (AI Platform), batch and real-time data processing (Dataflow, Pub/Sub, and Dataproc), and visual analytics (Google Looker Studio). Google Cloud big data solutions are serverless, which removes complexity and increases the ease of use.
- Global network
- Google Cloud networks have global availability by default and are scaled according to software-defined solutions, instantly responding to users’ needs.
- Environment friendly
- Google Cloud data centers run on 100% renewable energy where it is available. Since 2017, Google has been carbon neutral and has set the goal to run all its data centers carbon free 24/7/365 by 2030.
Recently, Google Cloud released carbon footprint tools, which allow customers to choose virtual machines (VMs) with low CO2 emissions, resulting in a lower carbon footprint.
In the following figure, we have an excellent example of this commitment. When creating a GCE VM, users can choose the Google Cloud region with the lowest CO2 consumption:
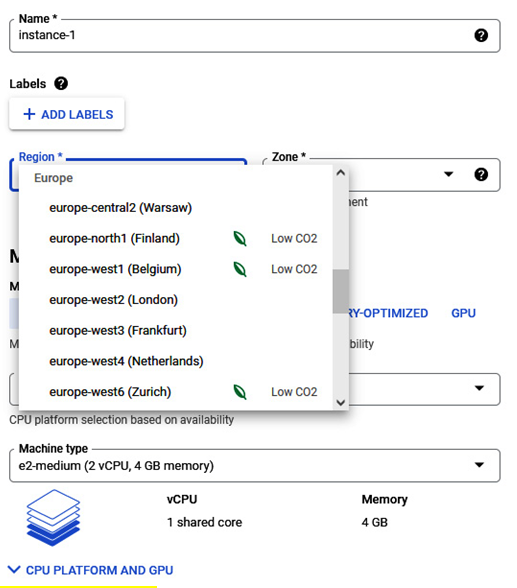
Figure 2.3 – The creation of the VM with a selection of regions with a low CO2 footprint
Google provides cloud sustainability reports at the following website: https://cloud.google.com/sustainability
This website is a great resource for anyone who would like to learn more about what Google did in the past to work toward carbon neutrality, and how Google wants all their data centers to be carbon free by 2030.
